The Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) market has been undergoing significant growth and transformation as industries continue to emphasize safety, quality assurance, and operational efficiency. NDT is an essential component in ensuring the integrity and performance of materials, components, and structures across various sectors, such as aerospace, automotive, manufacturing, energy, and infrastructure. With the rapid advancement of technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, and machine learning (ML), the NDT market is set for continued expansion.
What is Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)?
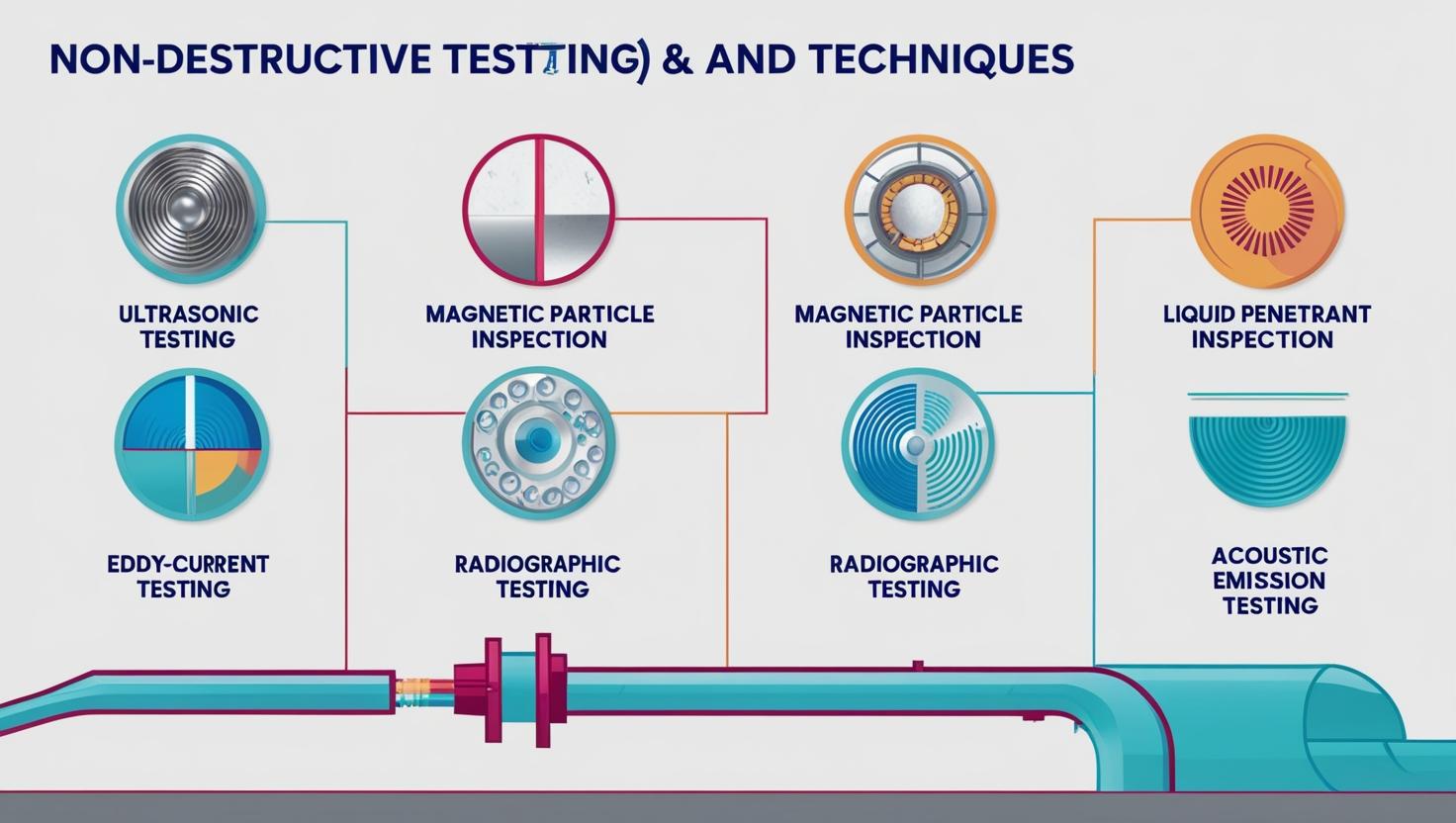
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) refers to the process of inspecting, testing, or evaluating materials or structures without causing any damage or altering their original state. The primary goal of NDT is to detect defects, corrosion, cracks, or other irregularities that could compromise the safety, reliability, or performance of an asset. Common NDT methods include ultrasonic testing, radiographic testing, magnetic particle testing, visual inspections, and eddy current testing, among others.
Market Growth and Demand
The global NDT market is witnessing robust growth, driven by increasing investments in infrastructure development, stricter safety regulations, and the demand for higher operational efficiencies.
The NDT and inspection industry is expected to reach USD 18.4 billion by 2029 from 11.6 billion in 2024, at a CAGR of 9.6% during the 2024-2029 period, as businesses and industries increasingly rely on NDT to maintain and manage their assets. The expanding adoption of automation technologies and AI-based solutions also plays a significant role in accelerating this growth.
Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=882
Key Factors Driving Market Growth
- Safety Regulations and Standards: With stricter safety regulations across industries, ensuring the integrity of assets has become a critical focus for organizations worldwide. Governments and regulatory bodies are enforcing safety standards that require regular and thorough inspections of equipment, structures, and materials, which drives the demand for NDT services.
- Aging Infrastructure: As infrastructure worldwide continues to age, maintaining and repairing critical assets such as bridges, pipelines, and power plants is increasingly important. NDT helps identify potential problems before they cause catastrophic failures, thus ensuring the longevity and safety of infrastructure.
- Technological Advancements: The integration of AI, IoT, robotics, and machine learning into NDT processes is significantly improving the accuracy and efficiency of inspections. AI-driven solutions, for example, can automatically analyze large sets of inspection data to identify potential defects, enhancing both the speed and precision of testing. Similarly, IoT sensors enable continuous monitoring, providing real-time data to predict potential failures before they occur.
- Cost Savings and Operational Efficiency: NDT helps reduce maintenance costs by identifying issues before they escalate into major problems. By preventing downtime, minimizing repairs, and optimizing asset performance, NDT enables companies to achieve cost savings and improve their bottom lines.
- Industry-Specific Applications: Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and energy are increasingly utilizing NDT for quality assurance, ensuring their products meet the highest standards. For example, in the aerospace industry, where even the smallest defect can be catastrophic, NDT is crucial in detecting cracks or corrosion in aircraft structures and components.
Key Trends in the NDT Market
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: AI is transforming the NDT market by enhancing data analysis and enabling more accurate defect detection. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and learn from past inspections, improving the system’s ability to predict potential issues and providing actionable insights for maintenance teams.
- IoT for Real-Time Monitoring: IoT sensors are revolutionizing the way NDT is performed. By embedding sensors into equipment and structures, companies can continuously monitor the condition of their assets in real-time. This ongoing data collection allows for predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and improving asset reliability.
- Robotics in NDT: Robotics is increasingly being used to carry out inspections in hazardous or difficult-to-reach environments, such as offshore rigs, pipelines, or high-rise buildings. These robots are equipped with advanced sensors and cameras, allowing for efficient, precise, and safe inspections.
- Automation and Smart NDT Solutions: The demand for automation in industries has led to the development of smart NDT systems that reduce the need for manual intervention. These systems are capable of conducting autonomous inspections, analyzing data, and generating reports with minimal human input. This not only increases inspection efficiency but also enhances the safety of workers in hazardous environments.
- Mobile and Remote NDT Solutions: With the rise of mobile technology, field inspectors are increasingly using mobile devices to perform and manage NDT activities. Remote monitoring tools enable experts to perform inspections from anywhere, providing real-time feedback and analysis.
Opportunities in the NDT Market
- Expansion in Emerging Markets: The growing industrialization in regions such as Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East presents a significant opportunity for the NDT market. As countries in these regions invest in infrastructure and industrial projects, the demand for NDT services is expected to rise.
- Increasing Adoption of Smart Manufacturing: The advent of Industry 4.0 is pushing for the adoption of smart manufacturing processes, where NDT technologies integrated with AI, IoT, and big data analytics are used to optimize production quality and efficiency.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact: As industries focus more on sustainability, NDT is playing a crucial role in assessing the health of equipment that supports environmental and renewable energy initiatives, such as wind turbines and solar panels. NDT helps ensure that these systems are operating at peak efficiency, reducing environmental risks.
Challenges in the NDT Market
While the NDT market is growing rapidly, several challenges remain. These include:
- High Initial Investment: Implementing advanced NDT systems and technologies, especially those based on AI and IoT, can require substantial investment, which may pose challenges for small- and medium-sized businesses.
- Skilled Labor Shortage: NDT requires highly skilled professionals to interpret inspection results accurately. The shortage of trained personnel may hinder the growth of the market, especially as new technologies require additional expertise.
- Standardization and Regulation: As NDT technologies evolve, ensuring that these innovations align with industry standards and regulatory requirements is essential. Regulatory bodies need to establish clear guidelines to ensure the safe and effective use of new NDT methods.
The NDT market is poised for significant growth, driven by advancements in technology, increasing safety regulations, and the need for efficient, cost-effective asset management. AI, IoT, robotics, and automation are revolutionizing the industry by enhancing inspection accuracy, reducing costs, and improving operational efficiency. As industries continue to adopt these innovations, the NDT market will continue to expand, offering numerous opportunities for growth and innovation across various sectors.
The future of NDT lies in the seamless integration of advanced technologies, creating a smarter, more efficient approach to maintaining and ensuring the safety of critical assets. Organizations that embrace these advancements will be better positioned to enhance their operations, minimize risks, and achieve long-term success in a competitive and ever-evolving landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) related to the Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) market:
1. What is Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)?
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) refers to a range of inspection methods used to assess the properties and integrity of materials, structures, or components without causing damage. NDT is used to detect defects, cracks, or signs of wear in critical assets to ensure their safety and functionality.
2. What industries use NDT?
NDT is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, manufacturing, energy, construction, infrastructure, and oil & gas. It is particularly crucial in sectors that require the continuous safety and reliability of materials and equipment, including power plants, pipelines, bridges, and aircraft.
3. How does NDT work?
NDT works by using various techniques such as ultrasonic testing, radiographic testing, eddy current testing, visual inspections, and magnetic particle testing. These methods allow technicians to identify flaws or defects without compromising the structure or material being tested.
4. What are the advantages of using NDT?
- Safety: NDT ensures the structural integrity of assets and identifies potential risks before they become serious issues.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Prevents expensive repairs and downtime by identifying problems early.
- No Damage: Unlike destructive testing, NDT does not alter or damage the material being tested.
- Efficiency: Provides quick and accurate results, helping businesses save time and resources in the long run.
5. What are the key trends shaping the NDT market?
Key trends in the NDT market include:
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning: These technologies are enhancing defect detection, automating analysis, and improving predictive maintenance.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT-enabled sensors allow real-time monitoring and continuous assessment of critical infrastructure.
- Robotics and Drones: Drones and robots are being used for inspections in hazardous, difficult-to-reach areas, improving both safety and efficiency.
- Automation and Smart Systems: Increasing automation of inspection processes is leading to faster, more accurate results with minimal human intervention.
